Smart factories, also known as Industry 4.0 or the fourth industrial revolution, represent a new era in manufacturing characterized by the integration of advanced technologies to enhance efficiency, productivity, and flexibility. These factories leverage technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), big data, robotics, and automation to create a more connected and intelligent production environment.
Key components of smart factories include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting machines, devices, and sensors to collect and exchange data in real-time. This enables better monitoring and control of the manufacturing processes.
- Big Data and Analytics: Analyzing large sets of data generated by various processes to gain insights, optimize production, and make informed decisions.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Implementing AI and ML algorithms to automate decision-making processes, predict equipment failures, and optimize production schedules.
- Automation and Robotics: Using robots and automated systems for tasks such as assembly, packaging, and quality control to increase efficiency and reduce human error.
- Cloud Computing: Storing and accessing data and applications over the internet, facilitating real-time collaboration and accessibility of information.
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Integrating physical processes with computer-based algorithms and software to create a more responsive and adaptive manufacturing environment.

The adoption of smart factories is indeed a growing trend across industries. Many companies recognize the potential benefits of increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved quality that come with embracing Industry 4.0 technologies. Mitsubishi Electric is a great example of this. Their Thailand-based prototype factory, created in collaboration with True 5G and LERTVILAI, incorporates high-speed data processing and inspection of production lines as well as autonomous mobile robots, AR, and VR to boost performance of production lines.
We are seeing several industries emerging at the forefront of adopting such concepts, including:
- Automotive: Implementing advanced robotics and automation for assembly lines and integrating smart technologies for quality control.
- Electronics: Using smart factories to improve precision in manufacturing processes and enhance product quality.
- Aerospace: Leveraging smart manufacturing for precision machining, monitoring equipment health, and optimizing supply chain logistics.
- Pharmaceuticals: Employing advanced analytics and IoT to monitor and improve production processes, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
As with any new technology or trend, Industry 4.0 has its challenges. For example:
- Implementation Costs: Initial investment in technology and infrastructure can be substantial.
- Security Concerns: Increased connectivity raises cybersecurity risks, requiring robust security measures.
- Workforce Skill Gaps: Employees may need training to adapt to new technologies and workflows.
- System Integration Issues: Incorporating from different vendors into one cohesive, functioning, and reliable system is often difficult and requires highly skilled IT experts.

Why Companies Should Consider Smart Factories:
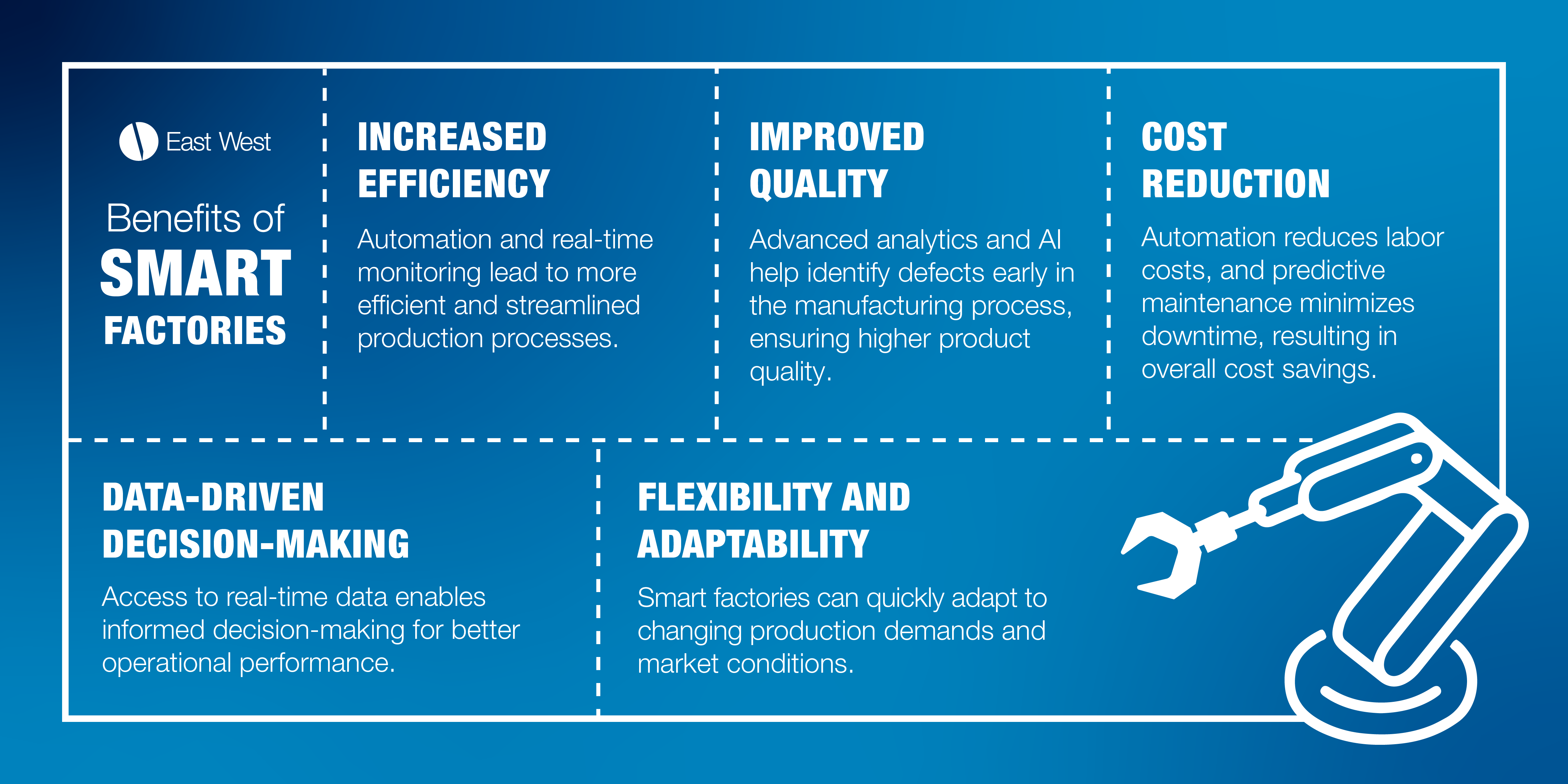
Adopting smart factory technologies can provide a competitive edge in terms of efficiency, quality, and innovation. Automation and real-time monitoring lead to more efficient and streamlined production processes, while access to real-time data enables informed decision-making for better operational performance.
Yes, this is not a cheap migration and initial investment is significant. However, the long-term benefits of reduced operational costs and increased productivity can be substantial. Automation reduces labor costs, while predictive maintenance minimizes downtime, all leading to overall cost savings. And that is just the tip of the iceberg.
Smart factories enable companies to respond quickly to market changes and customer demands. Now more than ever, we have learned how agility and responsiveness are imperative qualities to sustain success in times of changing production demands and supply chain disruptions.
Finally, advanced monitoring and analytics contribute to improved product quality and reliability. With humans performing much of the workload, it is inevitable that errors will occur. However, when companies leverage AI, they can help identify defects early in the manufacturing process.
As Industry 4.0 spreads throughout the world’s most popular manufacturing geographies, smart factories will continue to develop as companies are driven by the potential for increased efficiency, cost savings, and improved competitiveness. Sure, it will be a slow process before smart factories are common practice, and there will be growing pains and inevitable challenges to overcome, but the benefit of smart manufacturing remains a compelling choice for companies looking to stay at the forefront of their industries.




.jpg?width=176&height=56&name=MR_associatedNetwork_logo%20(1).jpg)