To protect a printed circuit board (PCB) from the elements, including moisture, dust and extreme temperatures, conformal coatings are often applied. But there are several types to choose from, so how can you be certain you're making the right call? Below we'll cover the five main types of coating, as well as advantages and disadvantages of each.
What is Conformal Coating?
Conformal coating is a polymeric film that covers, and conforms to, circuit board components and other electronics. Its primary purpose is to protect electronics from environmental elements and corrosion. The coating acts as both a protective shield and insulative material for a PCB.
Benefits of Conformal Coating
Humiseal.com outlines the following benefits of coating your PCB:
- Insulating properties allow a reduction in PCB conductor spacing of over 80%
- Can help eliminate the need for complex, sophisticated enclosures
- Light weight
- Completely protect the assembly against chemical and corrosive attack
- Eliminate potential performance degradation due to environmental hazards
- Minimize environmental stress on a PCB assembly
Types of Conformal Coating
While many varieties of coating exist – including a few specialty types – there are five main categories based on the substances' chemical makeup. The categories are: urethane resin (UR), epoxy resin (ER), acrylic resin (AR), silicone resin (SR) and parylene (XY). Below are descriptions, pros and cons of each. When selecting a coating, the most critical consideration should be the application and required functionality of your electronics within that application.
Urethane Resin (UR)
Urethane resins can be either single- or double-part substances.

Acrylic Resin (AR)
Acrylic resins are preformed acrylic polymers that have been dissolved in a solvent (source: ACI Technologies). They are typically one-part substances.
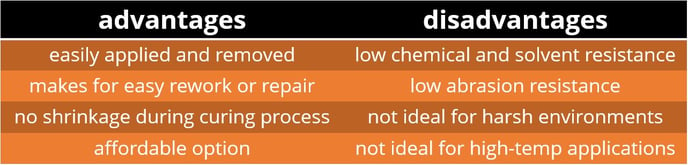
Epoxy Resin (ER)
Urethane coatings are usually two-part compounds, although one-part varieties are also available.
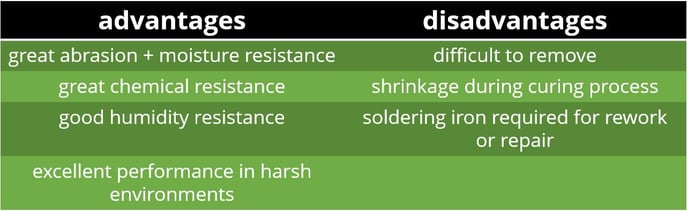
Silicone Resin (SR)
Silicone resin coatings are single-component compounds that are often chosen for electronics that will be subjected to extreme temperature ranges.
![]()
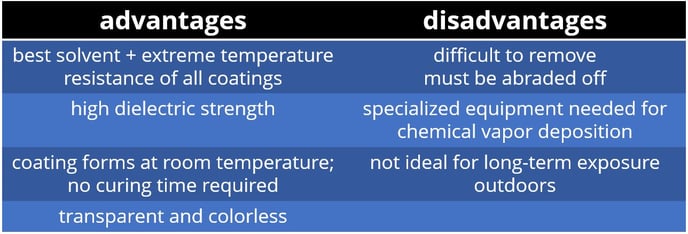
Parylene (XY)
Parylene coatings are applied through a process called chemical vapor deposition. Parylene becomes a gas when heated. After cooling, it is put into a vacuum chamber, where it polymerizes and turns into a film. The film is then placed over the electronics.
Conclusion
Remember, when choosing a coating for your printed circuit board or other electronics, keep the application and the electronics' functional requirements in mind. Protecting the board is important, but protecting it with the appropriate material is crucial. Consider the environmental conditions and rework or repair needs when selecting a coating type.
References and Additional Resources:
ACI Technologies, Inc.
Chemtronics
Diamond-MT blog
Further Reading:
Think Twice Before Seeking Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) on Alibaba
3 Things Product Development Engineers Want More Than "Fast"




.jpg?width=176&height=56&name=MR_associatedNetwork_logo%20(1).jpg)